

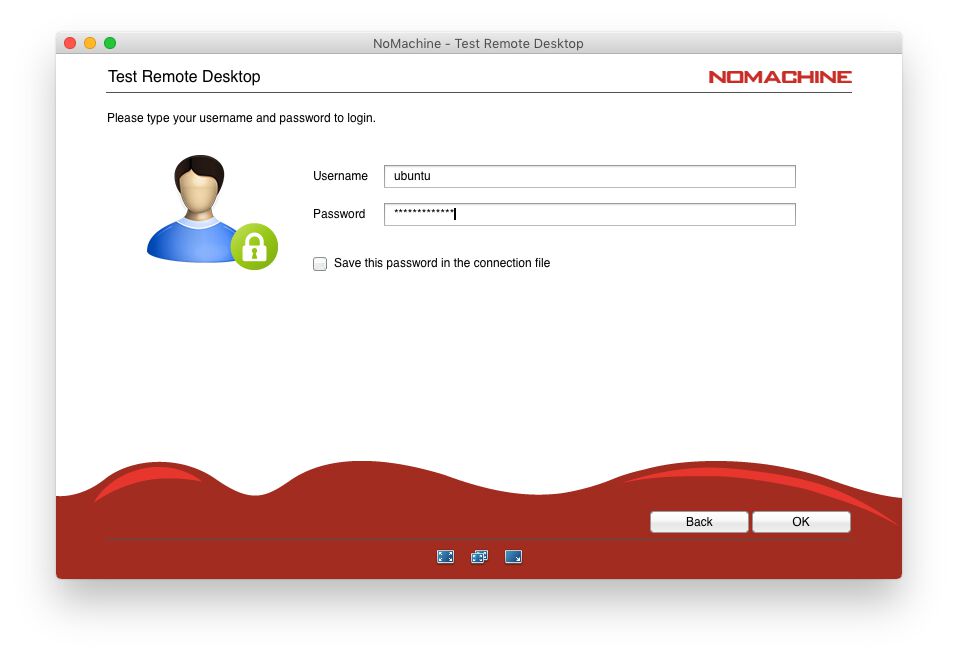
From the main application window, click +Add.Start the NoMachine application on your computer.On your local computer, download and install the NoMachine package for your operating system.If you changed the port to 7000, for example: $ sudo ufw allow 7000 If you did not change the port: $ sudo ufw allow 4000 Uncomment it and change it to: NXPort 7000Īllow the NoMachine port through the firewall. Locate the following configuration line: #NXPort 4000 For example, to change the port to 7000:Įdit the main configuration file using a text editor of your choice. The default port for NoMachine is 4000, but you can change the port if needed. Configure the FirewallĬhanging the port number in the next four steps is optional. NoMachine is now installed on your server and ready to receive connections. NX> 700 NoMachine was configured to run the following services: NX> 700 Creating configuration in: /usr/NX/etc/server.cfg. NX> 700 Install log is: /usr/NX/var/log/nxinstall.log. NX> 700 Using installation profile: Debian. Output: NX> 700 Installing: nxserver version: 7.9.2. If you use those methods, make note of where you upload the file.Ĭonnect to the server as your sudo user with SSH.Ĭhange to the /tmp directory, or where you uploaded the package. $ scp ~/Downloads/nomachine_b can also use SFTP, or a graphical program like Filezilla or Cyberduck to copy the package to the server. Assuming you downloaded it to ~/Downloads on your local machine, you can copy it the server /tmp directory with scp. Make note of the download location on your local machine.Ĭopy the package to the server. Open a web browser and download the NoMachine for Linux deb amd64 package from the official website.When the server reboots, it will end your SSH connection. Reboot the server for the changes to take effect.

You should see output like this: Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/default.target â /lib/systemd/system/graphical.target. $ sudo systemctl set-default graphical.target Switch the server from a terminal-based environment to the desktop environment. Verify that Gnome is running by checking the service status. $ sudo apt install xfonts-100dpi xfonts-100dpi-transcoded xfonts-75dpi xfonts-75dpi-transcoded xfonts-base Connect to the server as your sudo user with SSH.Create a standard user with sudo privileges.You'll have better performance if you use a server with more RAM. Deploy a new Debian 11 server with at least 2 GB of RAM.This guide explains how to create a virtual desktop on a Debian server with NoMachine, a remote desktop application. A Virtual Desktop hosted in the cloud is useful for many applications.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
